A Building Envelope Test, also known as a building enclosure test or building envelope commissioning, is a procedure used to assess the performance of a building’s envelope, which includes the exterior walls, roof, windows, doors, and other components that separate the interior and exterior environments. The test is typically performed by building professionals or specialized contractors and involves evaluating the integrity and effectiveness of the building’s interior and exterior in terms of air leakage, water penetration, and thermal performance.
Here’s an overview of how a Building Envelope Test is usually performed:
- Preparation: Before conducting the test, the building envelope is inspected, and any potential issues, such as damaged seals or openings, are identified and repaired.
- Equipment setup: The building is depressurized or pressurized using specialized equipment, such as a blower door fan, to create a pressure difference between the interior and exterior of the building.
- Air leakage test: For a depressurization test, the blower door fan is installed in an exterior door opening, and the interior air is drawn out to create negative pressure. In the case of pressurization, the fan is used to blow air into the building to create positive pressure. During this process, airflow rates are measured, and the building envelope’s air-tightness is assessed.
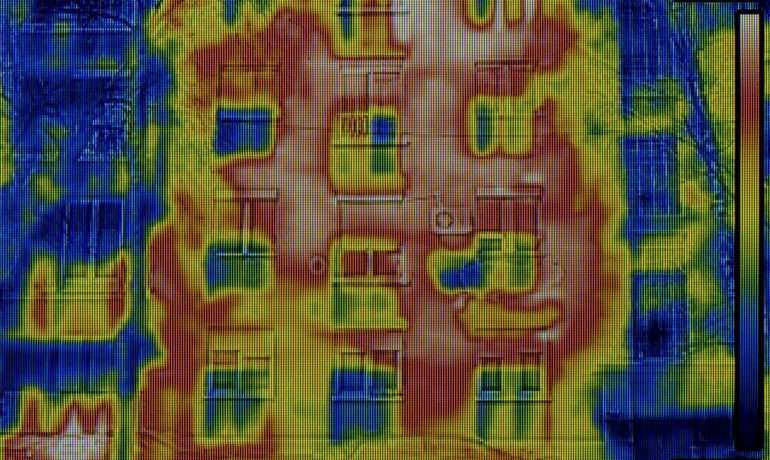
- Thermal imaging: Thermal imaging cameras may be used to identify areas of heat transfer, which can indicate insulation deficiencies or air leakage points in the building envelope.
- Water penetration test: This test involves simulating rainfall or spraying water onto the exterior surfaces of the building envelope to assess its ability to resist water infiltration.
- Data analysis: The data collected during the tests are analyzed to determine the overall performance of the building envelope and identify any weaknesses or areas for improvement.
When would it be necessary?
A Building Envelope Test is necessary in several situations:
- New construction: It is often required by building codes and standards to conduct these tests on new constructions to ensure they meet performance criteria for energy efficiency, air quality, and water resistance.
- Building renovation or retrofitting: When major renovations or retrofitting projects are carried out, this test can help identify if any upgrades are needed to improve energy efficiency or address any potential water or air leakage issues.
- Troubleshooting: If occupants are experiencing comfort issues, such as drafts or inconsistent temperatures, this test can help pinpoint the root causes and suggest remedies.
- Energy efficiency improvements: As part of energy efficiency audits, these tests can help evaluate the effectiveness of insulation and identify areas where energy losses are occurring.
- Compliance with green building standards: For buildings seeking certifications like LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design), this test might be required to demonstrate compliance with certain performance criteria.
In summary, a Building Envelope Test is an important procedure to assess the performance of a building’s envelope in terms of air leakage, water penetration, and thermal efficiency. It helps ensure buildings are energy-efficient, comfortable, and meet regulatory standards and certifications.